Oxidative Stress and Inborn Errors of Metabolism
Main Article Content
Abstract
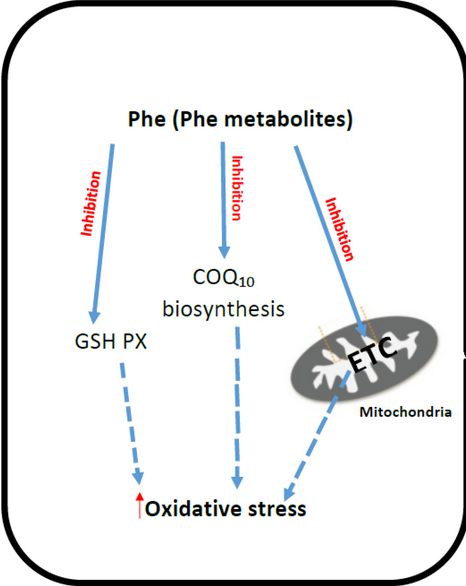
Oxidative stress has been demonstrated to be an underlying patho-physiologic process in various inborn errors of metabolism. Metabolic profiling of oxidative stress may provide a nonspecific measure of disease activity that may further enable physicians to monitor disease. In this study, we try to find the correlation between the oxidative stress and inborn. Quantifying oxidative stress offers a unique perspective to IEM. Certain measures may provide a means of addressing mitochondrial function in IEM and aid in the development of therapeutic targets and clinical monitoring in this diverse set of disorders.
Article Details
References
Stenton SL, Kremer LS, Kopajtich R, Ludwig C, Prokisch H. The diagnosis of inborn errors of metabolism by an integrative "multi-omics" approach: A perspective encompassing genomics, transcriptomics, and proteomics. J Inherit Metab Dis. 2020 Jan;43(1):25-35.
Marques EP, Wyse ATS. Creatine as a Neuroprotector: an Actor that Can Play Many Parts. Neurotox Res. 2019 Aug;36(2):411-423.
Guerrero RB, Kloke KM, Salazar D. Inborn Errors of Metabolism and the Gastrointestinal Tract. Gastroenterol Clin North Am. 2019 Jun;48(2):183-198.
Canton M, Gall DL, Feillet F, Bonnemains C, Roy A. Neuropsychological Profile of Children with Early and Continuously Treated Phenylketonuria: Systematic Review and Future Approaches. J Int Neuropsychol Soc. 2019 Jul;25(6):624-643.
Mak CM, Lee HC, Chan AY, Lam CW. Inborn errors of metabolism and expanded newborn screening: review and update. Crit Rev Clin Lab Sci. 2013 Nov. 50 (6):142-62.
Argmann CA, Houten SM, Zhu J, Schadt EE. A Next Generation Multiscale View of Inborn Errors of Metabolism. Cell Metab. 2016 Jan 12. 23 (1):13-26.
Pizzino G, Irrera N, Cucinotta M, Pallio G, Mannino F, Arcoraci V, Squadrito F, Altavilla D, Bitto A. Oxidative Stress: Harms and Benefits for Human Health. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2017;2017:8416763. doi: 10.1155/2017/8416763. Epub 2017 Jul 27. PMID: 28819546; PMCID: PMC5551541.
W. Droge, “Free radicals in the physiological control of cell function,” Physiological Reviews, vol. 82, pp. 47–95, 2002.
J. K. Willcox, S. L. Ash, and G. L. Catignani, “Antioxidants and prevention of chronic disease,” Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition, vol. 44, pp. 275–295, 2004.
P. Pacher, J. S. Beckman, and L. Liaudet, “Nitric oxide and peroxynitrite in health and disease,” Physiological Reviews, . 87, pp. 315–424, 2007.
M. Genestra, “Oxyl radicals, redox-sensitive signaling cascades and antioxidants,” Cellular Signalling, vol. 19, pp. 1807–1819, 2007.
B. Halliwell, “Biochemistry of oxidative stress,” Biochemical Society Transactions, vol. 35, pp. 1147–1150, 2007.
I. Young and J. Woodside, “Antioxidants in health and disease,” Journal of Clinical Pathology, vol. 54, pp. 176–186,2001.
Bird S, Miller NJ, Collins JE, Rice-Evans CA. Plasma antioxidant capacity in two cases of tyrosinaemia type 1: one case treated with NTBC. J Inherit Metab Dis 1995;18:123–126.
Ercal N, Aykin-Burns N, Gurer-Orhan H, McDonald JD. Oxidative stress in a phenylketonuria animal model. Free Radic Biol Med 2002;32:906–911.
Streck EL, et al. Inhibition of rat brain Na+, K+-ATPase activity induced by homocysteine is probably mediated by oxidative stress. Neurochem Res 2001;26:1195–1200.
Wyse AT, et al. Nitric oxide synthase inhibition by L-NAME prevents the decrease of Na+,K+-ATPase activity in midbrain of rats subjected to arginine administration. Neurochem Res 2001;26:515–520.
Wyse AT, et al. Inhibition of Na(+),K(+)-ATPase activity in hippocampus of rats subjected toacute administration of homocysteine is prevented by vitamins E and C treatment. Neurochem Res2002;27:1685–1689.
Barschak AG, et al. Oxidative stress in plasma from maple syrup urine disease patients duringtreatment. Metab Brain Dis 2008;23:71–80. [PubMed: 18026828]
Barschak AG, et al. Evidence that oxidative stress is increased in plasma from patients with maplesyrup urine disease. Metab Brain Dis 2006;21:279–286.
Bridi R, et al. Induction of oxidative stress in rat brain by the metabolites accumulating in maplesyrup urine disease. Int J Dev Neurosci2003;21:327–332.
Bridi R, et al. alpha-keto acids accumulating in maple syrup urine disease stimulate lipidperoxidation and reduce antioxidant defences in cerebral cortex from young rats. Metab Brain Dis2005;20:155–167.
Wajner M, Latini A, Wyse AT, Dutra-Filho CS. The role of oxidative damage in the neuropathology of organic acidurias: insights from animal studies. J Inherit Metab Dis 2004;27:427–448. [PubMed: 15303000]
Sharma P, Kumar P, Tyagi MS, Sharma R, PS D. Prevalence of Inborn Errors of Metabolism in Neonates [Internet]. Journal of clinical and diagnostic research. JCDR Research and Publications; 2018.
L.R. Sirtori, C.S. Dutra-Filho, D. Fitarelli, A. Sitta, A. Haeser, A.G. Barschak, M. Wajner, D.M. Coelho, et.al,Oxidative stress in patients with phenylketonuria, Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Molecular Basis of Disease,Volume 1740, Issue 1, 2005,Pages 68-73,ISSN 0925 4439,https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbadis.2005.02.005
Ristoff, E. and Larsson, A. (2002), Oxidative stress in inborn errors of metabolism: Lessons from glutathione deficiency. J Inherit Metab Dis, 25: 223-226. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1015634032042
Artuch R, et al. A longitudinal study of antioxidant status in phenylketonuric patients. Clin Biochem2004;37:198–203. [PubMed: 14972641]
Cam, Veysel, et al. "Oxidative Stress in Intoxication Type Inborn Errors of Metabolism using Thiol-Disulfide Ratio." Journal of the College of Physicians and Surgeons Pakistan, vol. 31, no. 6, June 2021, pp. 663+. Gale Academic OneFile
Mcguire, Peter & Parikh, Aditya & Diaz, George. (2009). Profiling of Oxidative Stress in Patients with Inborn Errors of Metabolism. Molecular genetics and metabolism. 98. 173-80. 10.1016/j.ymgme.2009.06.007.
Colome C, et al. Lipophilic antioxidants in patients with phenylketonuria. Am J Clin Nutr2003;77:185–188. [PubMed: 12499340]
Delwing D, et al. Alpha-tocopherol and ascorbic acid administration prevents the impairment of brain energy metabolism of hyperargininemic rats. Cell Mol Neurobiol2006;26:177–189.[PubMed: 16619133]
Kosenko E, et al. Superoxide production and antioxidant enzymes in ammonia intoxication in rats. Free Radic Res 1997;27:637–644. [PubMed: 9455699]
Martinez-Cruz F, et al. Oxidative stress induced by phenylketonuria in the rat: Prevention by melatonin, vitamin E, and vitamin C. J Neurosci Res 2002;69:550–558. [PubMed: 12210848]
Ribeiro CA, et al. Inhibition of brain energy metabolism by the branched-chain amino acids accumulating in maple syrup urine disease. Neurochem Res 2008;33:114–124. [PubMed:17680360]